Sexually transmitted diseases (STDs) are a prevalent public health concern, emphasizing the importance of regular testing for early detection and treatment. Understanding how STD testing works is crucial for individuals seeking to take control of their sexual health. In this article, we unravel the process of STD testing, shedding light on the various methods and steps involved.
- Assessment and Counseling:The first step in the STD testing process typically involves a consultation with a healthcare professional. During this assessment, individuals can discuss their sexual history, potential exposure to STDs, and any symptoms they may be experiencing. This information helps healthcare providers determine the most appropriate tests for the individual’s circumstances.
- Choosing the Right Tests:Based on the assessment, healthcare providers will recommend specific tests tailored to the individual’s needs. Common STD tests include screenings for HIV, syphilis, chlamydia, gonorrhea, herpes (HSV), and human papillomavirus (HPV). The choice of tests may vary depending on factors such as symptoms, sexual activity, and potential exposure.
- Blood Tests:Blood tests are a common method for detecting antibodies or antigens associated with certain STDs, including HIV and syphilis. A small blood sample is drawn, and the blood is analyzed in a laboratory to identify any signs of infection.
- Urine Tests:Urine tests are frequently used for detecting chlamydia and gonorrhea. Individuals provide a urine sample, which is then tested for the presence of bacterial DNA or antigens. This method is non-invasive and convenient for both the patient and healthcare provider.
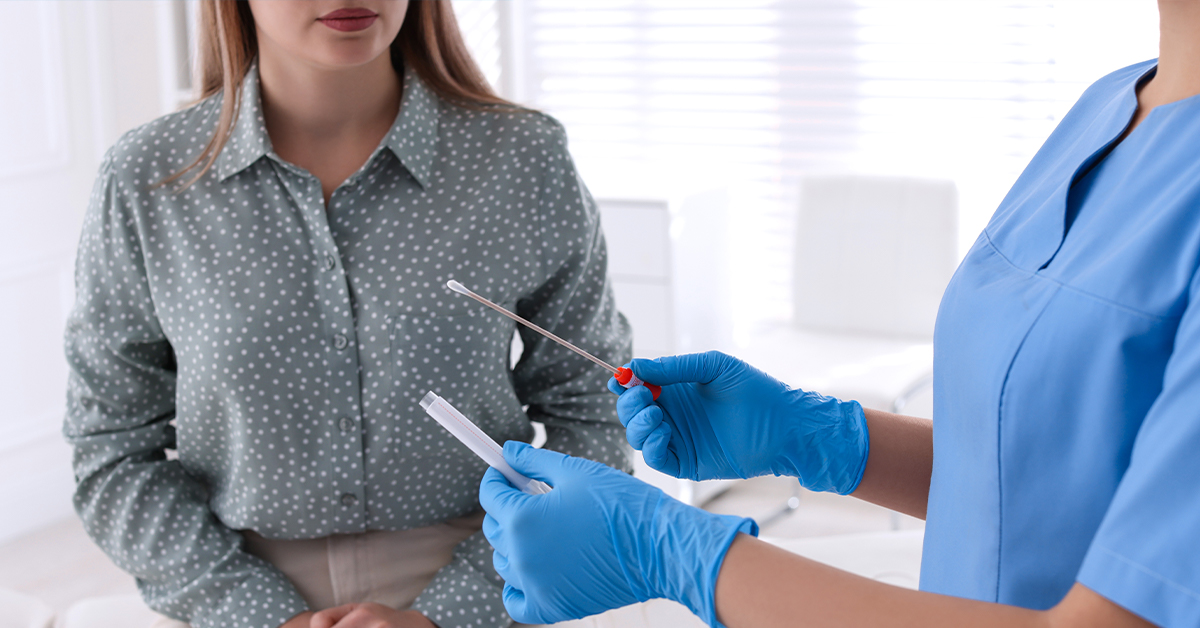
- Swab Tests:Swab tests involve collecting samples from the genital, oral, or rectal areas using a cotton swab. These samples are then analyzed for the presence of pathogens, making swab tests effective for detecting infections such as chlamydia, gonorrhea, and herpes.
- Rapid Tests:Rapid tests provide quick results, often within minutes, and are commonly used for HIV and syphilis. These tests may involve a small blood sample or an oral swab. Rapid tests are advantageous for immediate detection, especially in point-of-care settings.
- Home Testing Kits:Home testing kits have gained popularity, offering individuals the convenience of testing in the privacy of their own homes. These kits typically include instructions for collecting a sample (urine, blood, or swab), which is then sent to a laboratory for analysis. Home testing kits are available for various STDs, and results are often provided discreetly.
- Laboratory Analysis:Regardless of the testing method, collected samples are sent to a laboratory for analysis. Trained laboratory professionals conduct thorough examinations to identify any signs of infection. The accuracy of results depends on the specific testing method used and the expertise of the laboratory conducting the analysis.
- Post-Test Counseling and Treatment:Once results are available, individuals receive post-test counseling to discuss the outcomes and potential next steps. In the case of positive results, healthcare providers guide individuals through appropriate treatment options, emphasizing the importance of early intervention.
Conclusion:
STD testing is a crucial aspect of maintaining sexual health and preventing the spread of infections. The process involves a combination of assessment, choosing the right tests, sample collection, laboratory analysis, and post-test counseling. With advancements in technology and the availability of various testing methods, individuals can take proactive steps in preserving their well-being and that of their sexual partners. Seeking guidance from healthcare professionals ensures a comprehensive and personalized approach to STD testing.